Top 10 analyses to run with Simcenter Amesim engine models and how to choose the most suitable one
Thanks to its long history and expertise in the engine modeling area, Simcenter Amesim allows to model an internal combustion engine in many different ways, depending on the goals ...
We are used to talk about the scalability of Simcenter Amesim, but it goes way beyond this single word and we could say that the only purpose of this capability is to satisfy user’s needs.
Indeed, there are so many needs when it comes to engine modeling, and so many ways to model an engine in Simcenter Amesim, that without guidance, the user could choose an inappropriate submodel with the associated unwanted effects.
Here is a non-exhaustive list of the numerous ways a 4-cylinders engine model can be modeled, which user’s needs it satisfies and some hints about which one to choose based on several relative criterion.
Top 10 analyses to run with Simcenter Amesim engine models and how to choose the most suitable one
- #1 - Assessing the thermal behavior of an engine cooling and/or lubrication circuit
- #2 - Assessing the fluid flow behavior of an engine cooling and/or lubrication circuit
- #3 - Driving a pump, an alternator, a shaft or a power take-off
- #4 - Assessing the fuel consumption of the vehicle over a driving cycle
- #5 - Validating the Engine Control System
- #6 - Assessing the crankshaft torsional vibrations induced by the combustion
- #7 - Assessing the ride comfort and vehicle drivability
- #8 - Assessing the engine bearings lubrication
- #9 - Assessing the exhaust after-treatment system efficiency
- #10 - Assessing the engine air intake, exhaust and fuel systems performances
- Bonus (coming in rev 16) - Assessing the vehicle underhood thermal behavior
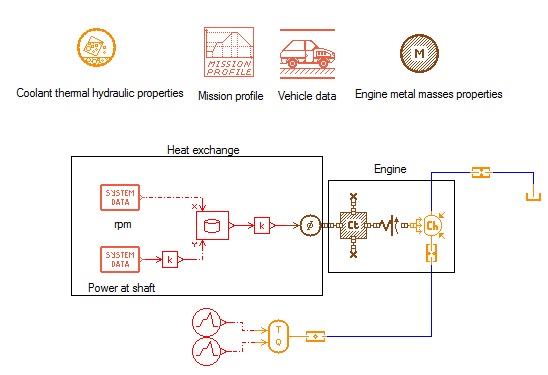
#1 - Assessing the thermal behavior of an engine cooling and/or lubrication circuit
The engine is a heat source and can be modeled using the following libraries and components:
- The Signal, Thermal and thermal hydraulic libraries components
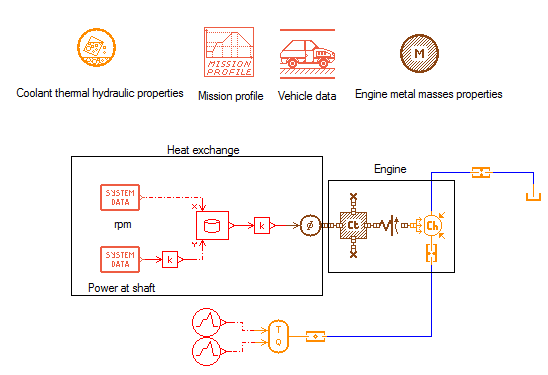 Simple Simcenter Amesim engine model for heat release
Simple Simcenter Amesim engine model for heat release
- Or the Cooling system library component
 Simple Simcenter Amesim engine model for heat release and cooling system design
Simple Simcenter Amesim engine model for heat release and cooling system design 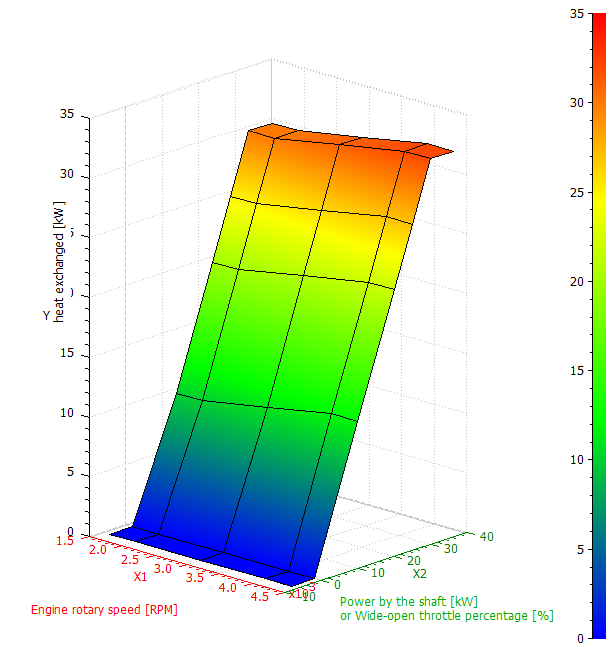 Heat release Simcenter Amesim map
Heat release Simcenter Amesim map
- Or the IFP-Drive library components
 IFP-Drive engine model for heat release
IFP-Drive engine model for heat release 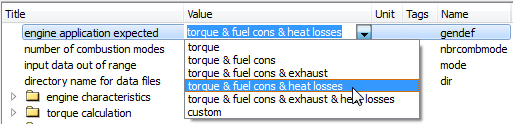 IFP-Drive engine model configuration for heat release computation
IFP-Drive engine model configuration for heat release computation
- Or the IFP-Engine library components (mean value engine model or high frequency engine model)
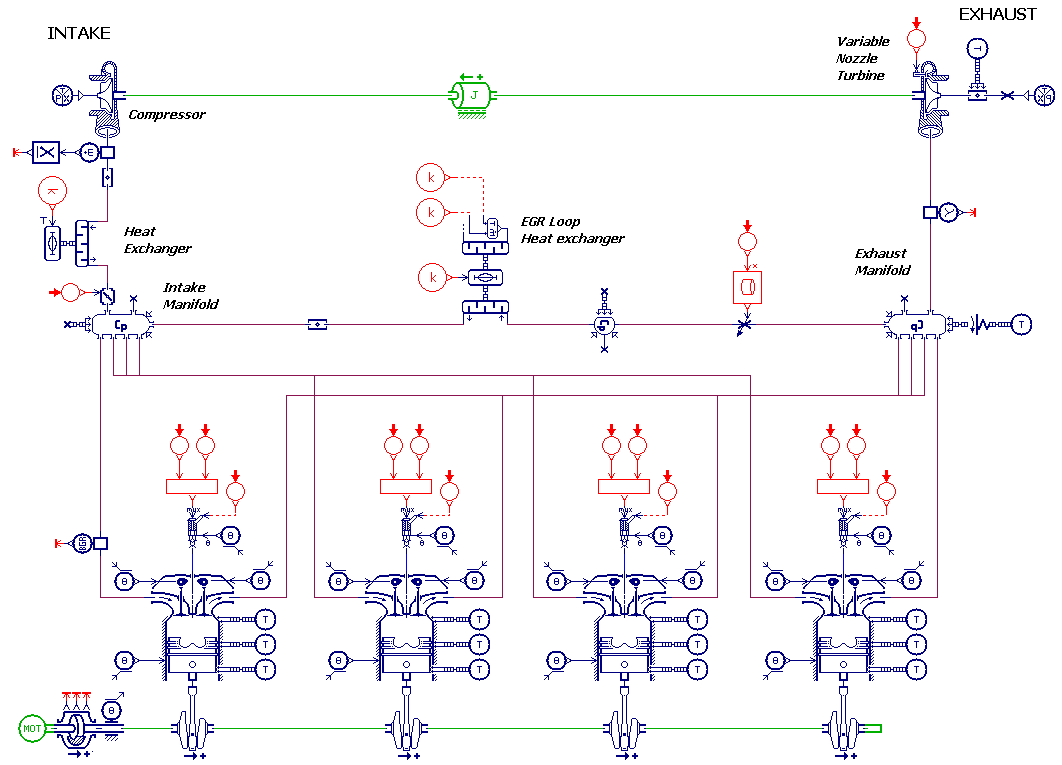
Capabilities summary 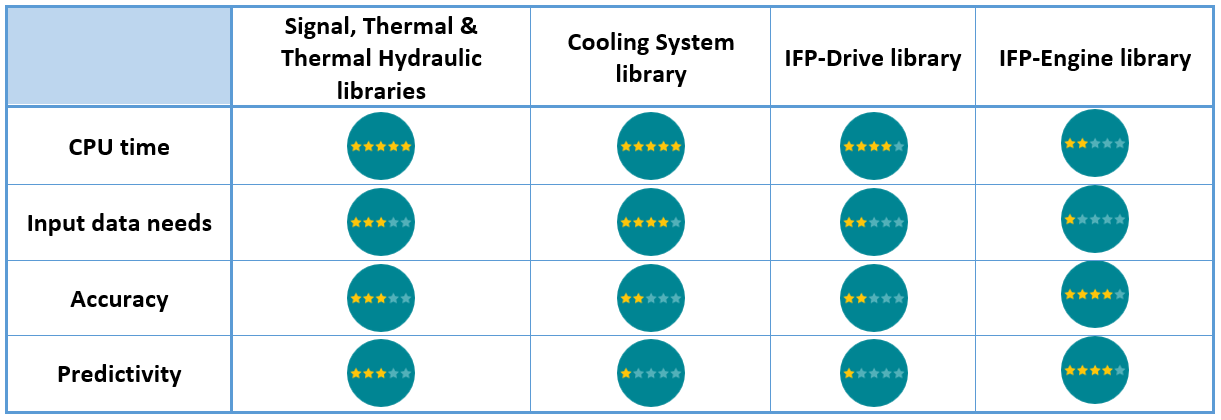
#2 - Assessing the fluid flow behavior of an engine cooling and/or lubrication circuit
The engine is a fluid volume with restrictions and can be modeled using the following libraries and components:
- The Signal, Thermal & Thermal Hydraulic libraries components
- Or the Cooling System library components
- Or the CAD import tool combined with Thermal and Thermal Hydraulic libraries components
Capabilities summary 
#3 - Driving a pump, an alternator, a shaft or a power take-off
The engine is a torque/rotational speed source and can be modeled using the following libraries and components:
- The Signal and Mechanical libraries components

- Or the IFP-Drive library components
- Or the Powertrain library components

- Or the IFP-Engine library components using a mean value engine model (MVEM)
Capabilities summary 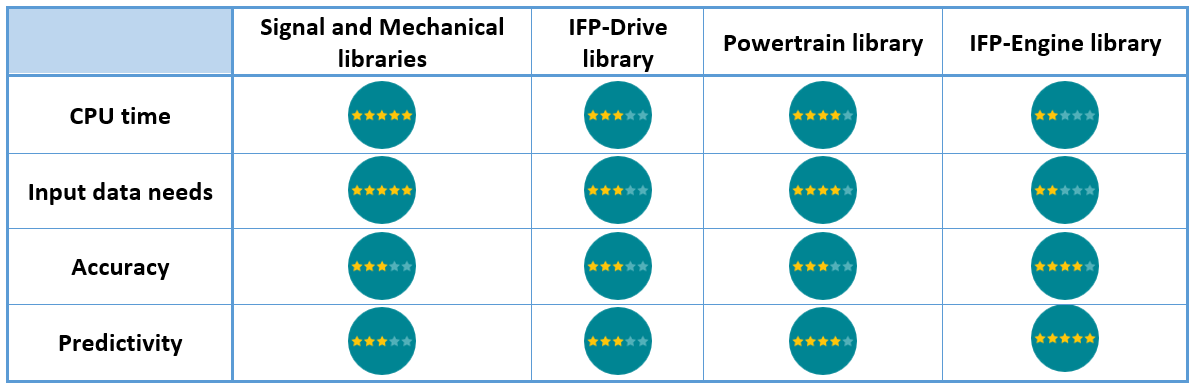
#4 - Assessing the fuel consumption of the vehicle over a driving cycle
The engine consumes fuel to drive the vehicle and can be modeled using the following libraries and components
- The IFP-Drive library components
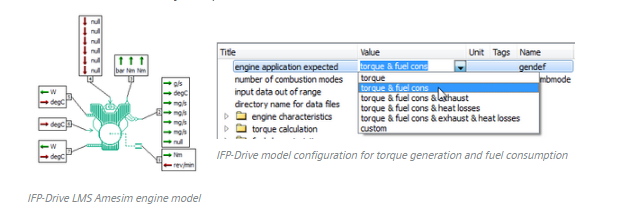
- Or the IFP-Engine library components using a Mean Value Engine Model (MVEM)
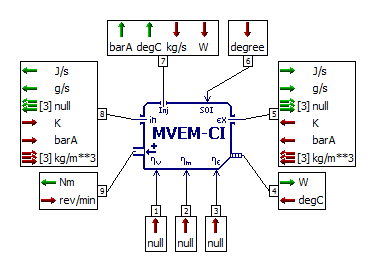
Simcenter Amesim Mean Value Engine model
- Or the IFP-Engine library components using a high frequency engine model
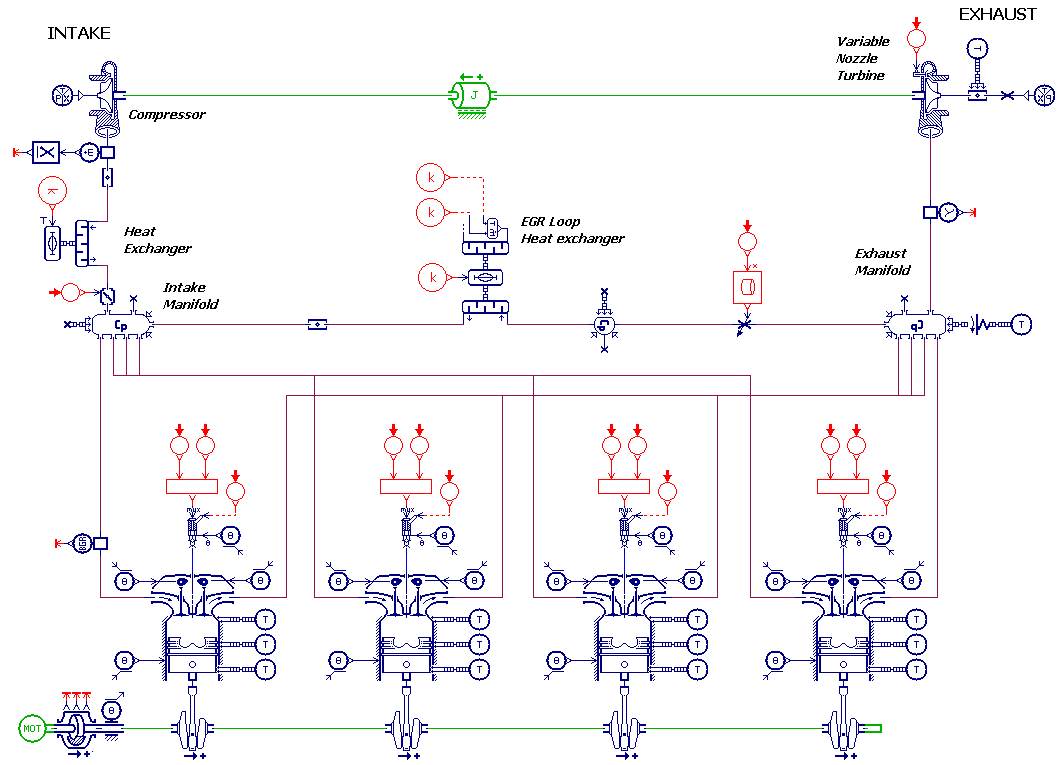
Detailed engine model for fuel consumption simulation in Simcenter Amesim Capabilities summary 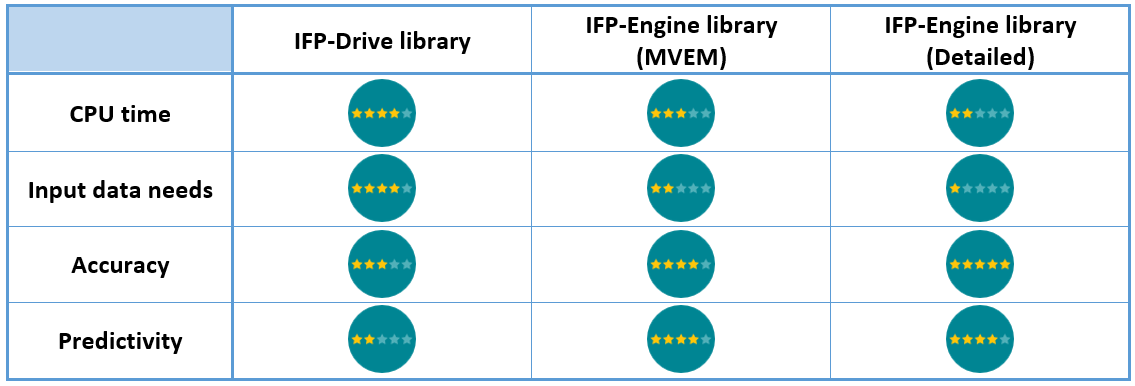
#5 - Validating the Engine Control System
The engine, its actuators and sensors are compatible with real-time control units and can be modeled using:
- IFP-Engine library components with MVEM
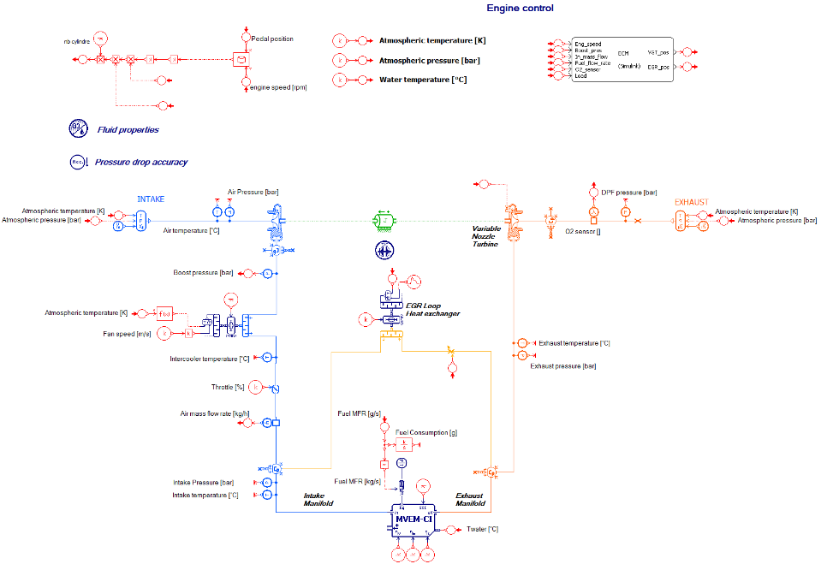
- Or with high frequency engine model
Capabilities summary 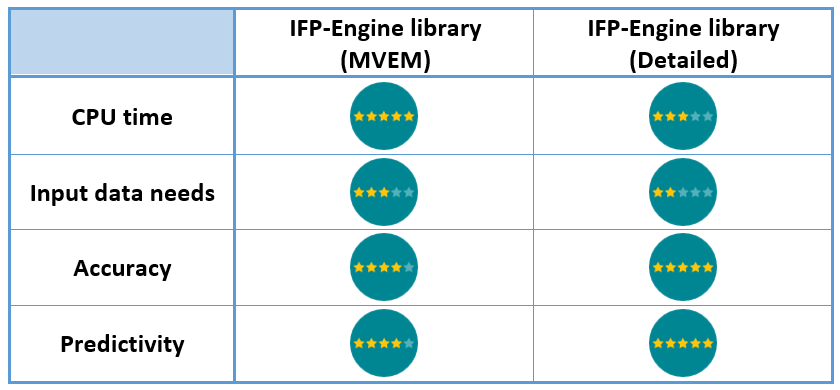
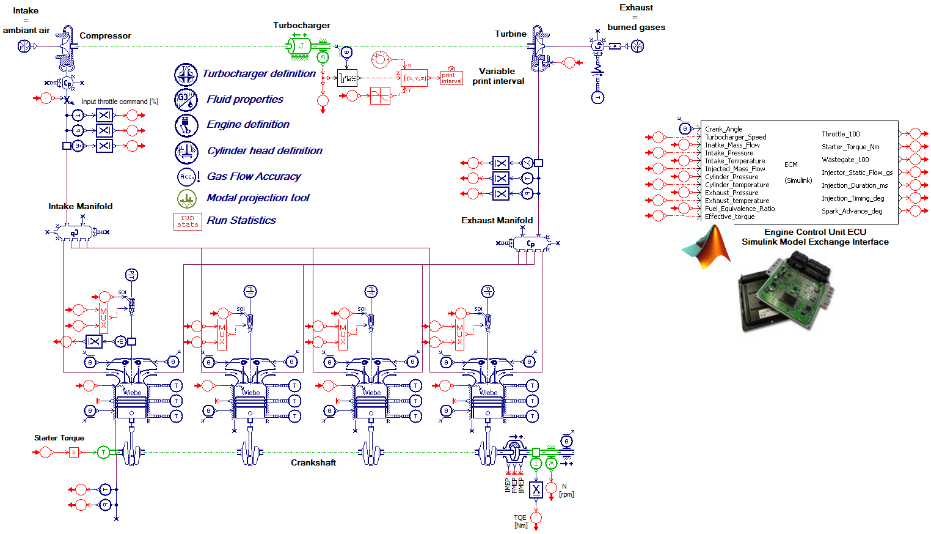
#6 - Assessing the crankshaft torsional vibrations induced by the combustion
The engine is a harmonics generator and can be modeled using the following libraries and components:
- The Powertrain library components

Simcenter Amesim engine model for NVH analysis
- Or the IFP-Engine library components
Capabilities summary 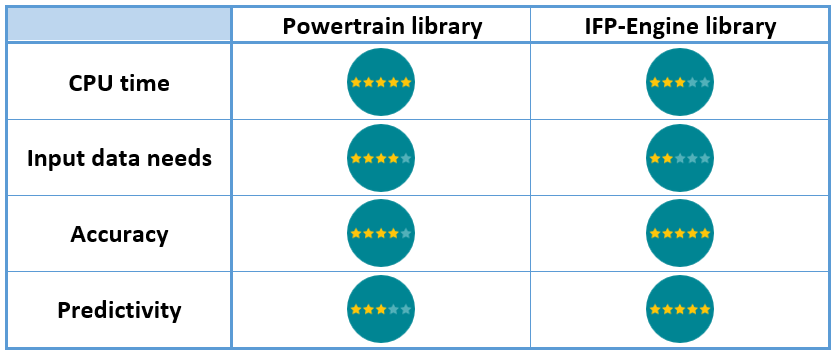
#7 - Assessing the ride comfort and vehicle drivability
The engine is a 3D dynamic mass with 6 degrees of freedom and can be modeled using:
- The Powertrain library components
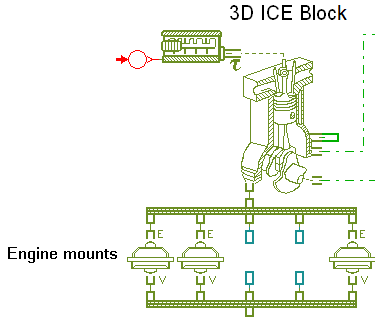
#8 - Assessing the engine bearings lubrication The engine is a reciprocating force source and can be modeled using the following libraries and components:
- The Planar Mechanical library components
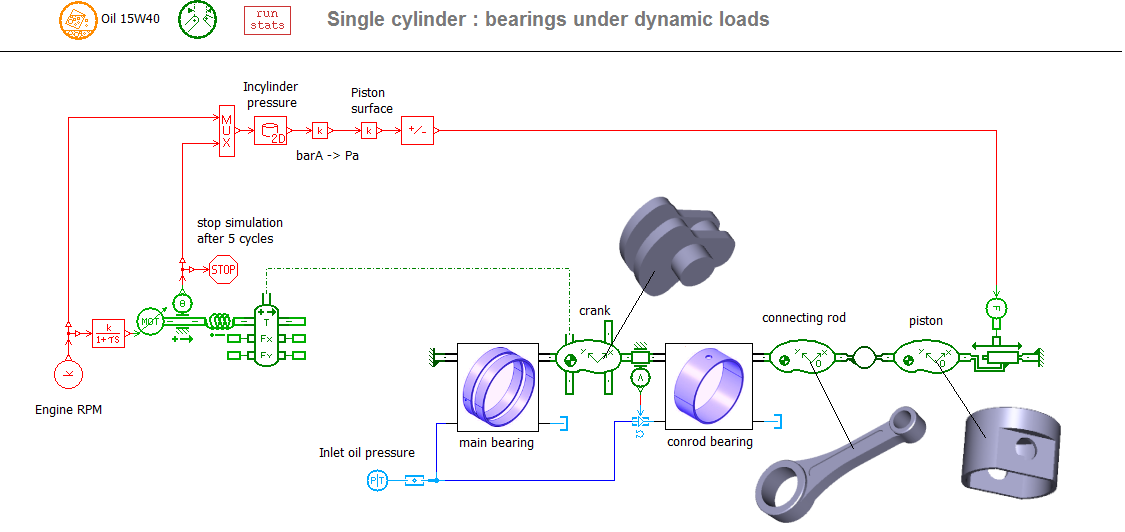
- Or the Powertrain library components

Capabilities summary 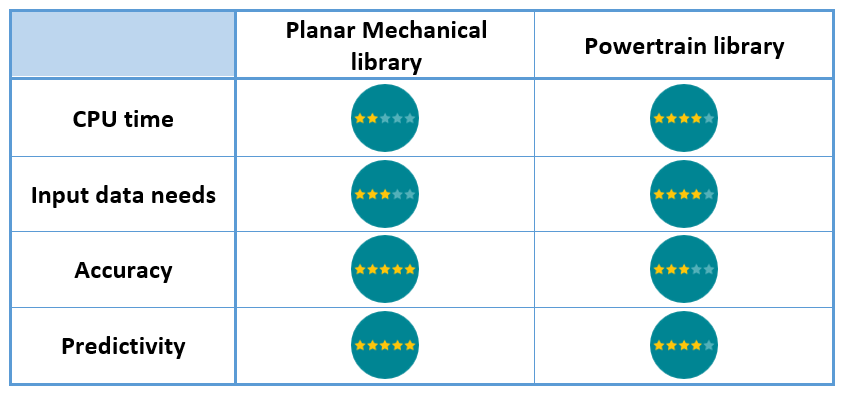
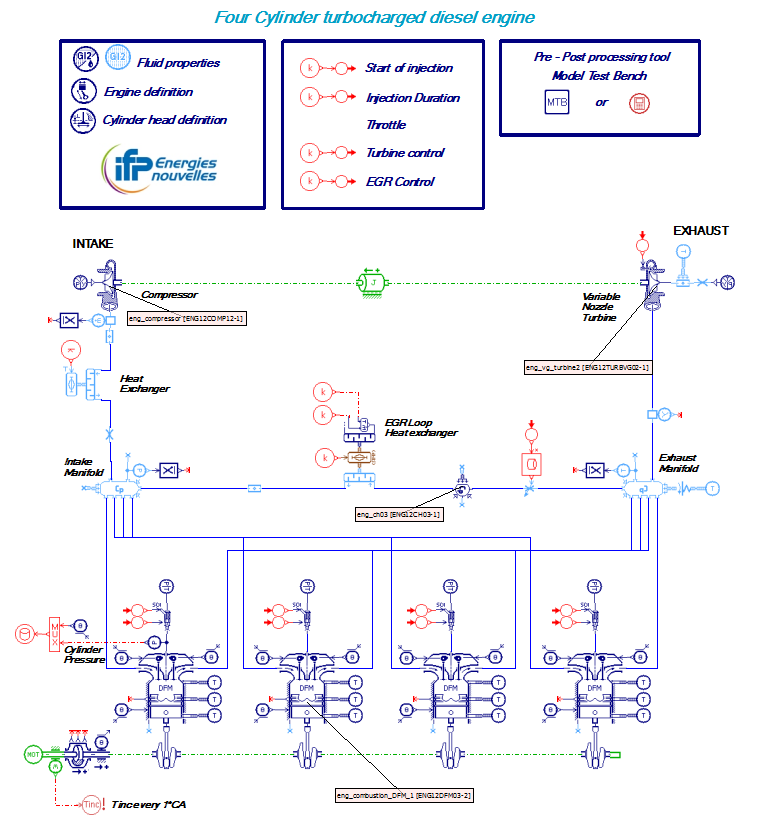
#9 - Assessing the exhaust after-treatment system efficiency
The engine is an exhaust gases generator and can be modeled using the following libraries and components:
- The Signal library components

- Or the IFP-Drive library components

- Or the IFP-Engine library components using MVEM
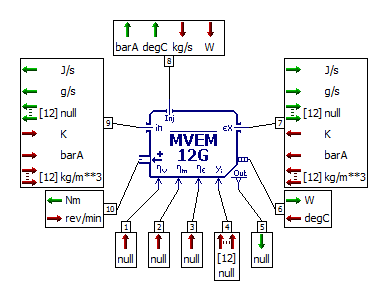
- Or the high frequency engine model
Capabilities summary 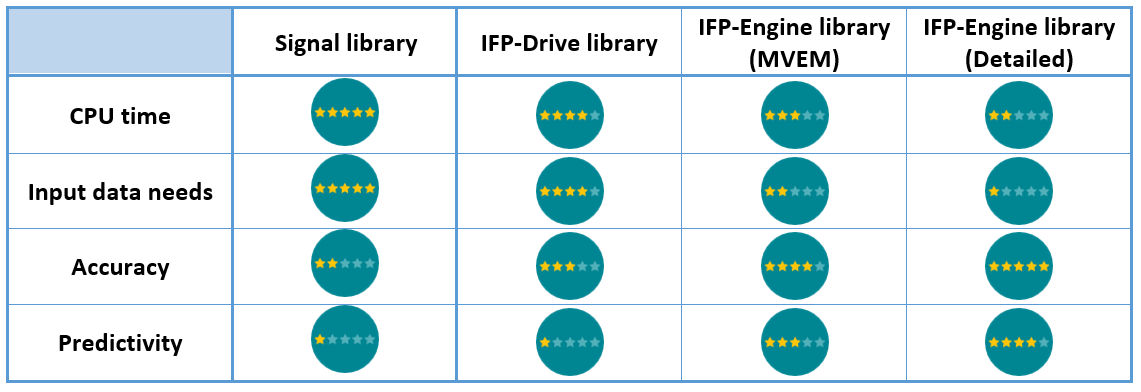
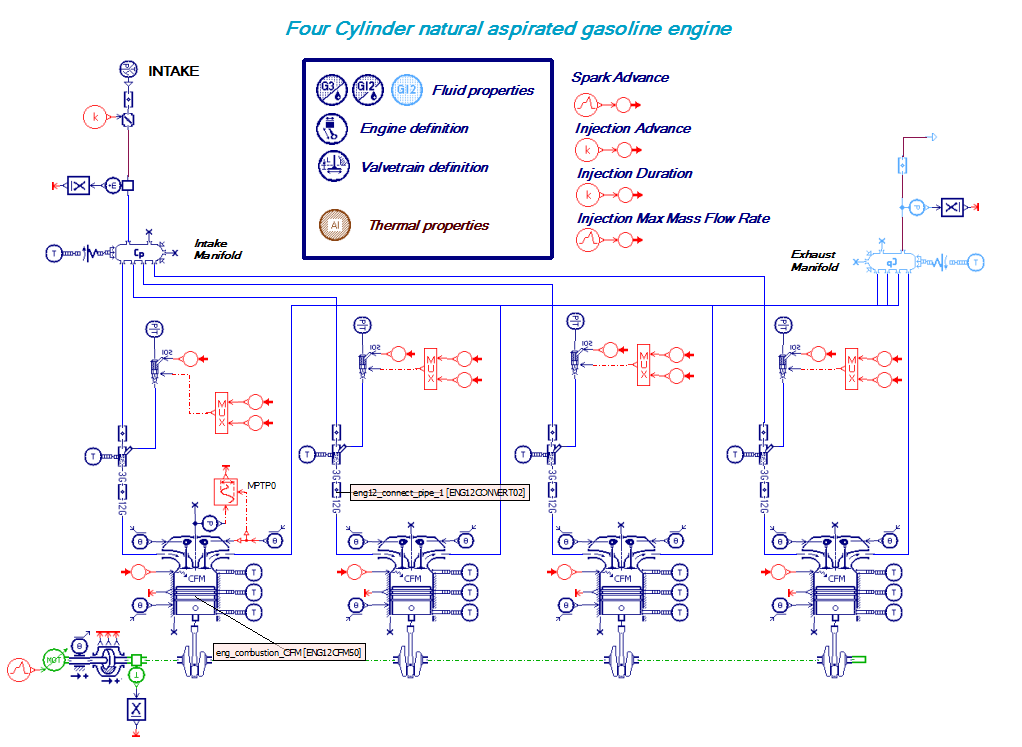
#10 - Assessing the engine air intake, exhaust and fuel systems performances
The engine converts air and fuel into exhaust gases, torque and heat and can be modeled using the following libraries and components:
- The IFP-Engine library components with MVEM
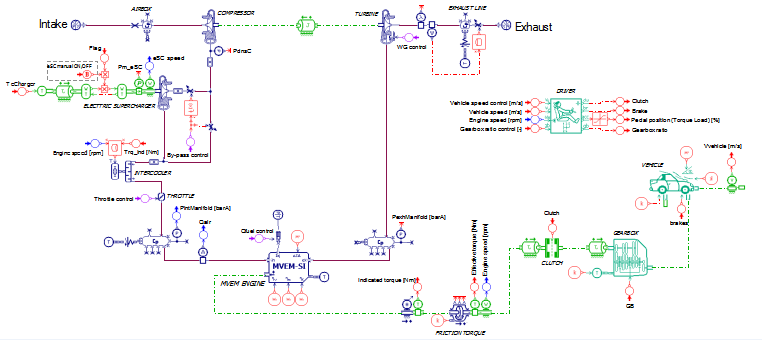
- Or the CFD 1D and IFP-Engine libraries components
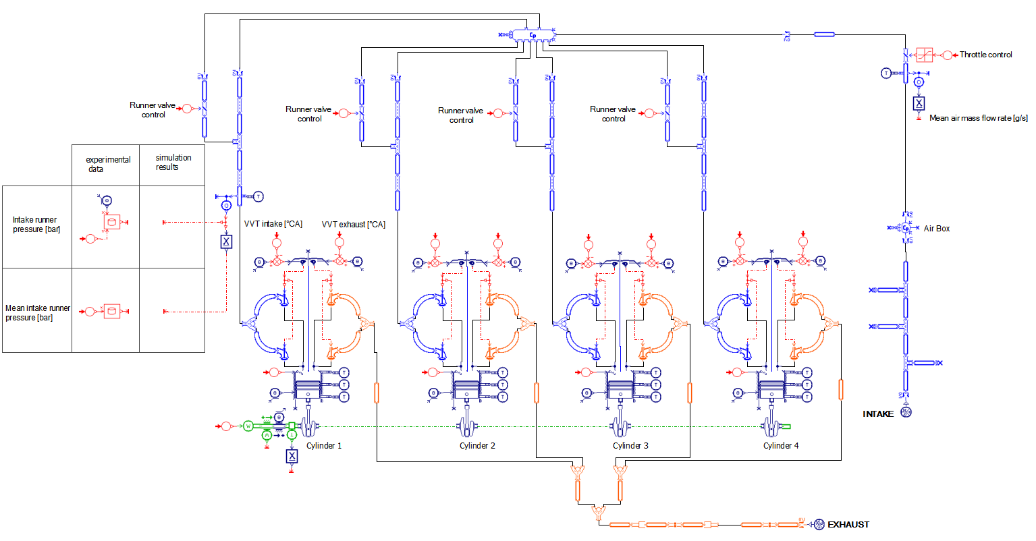
Capabilities summary 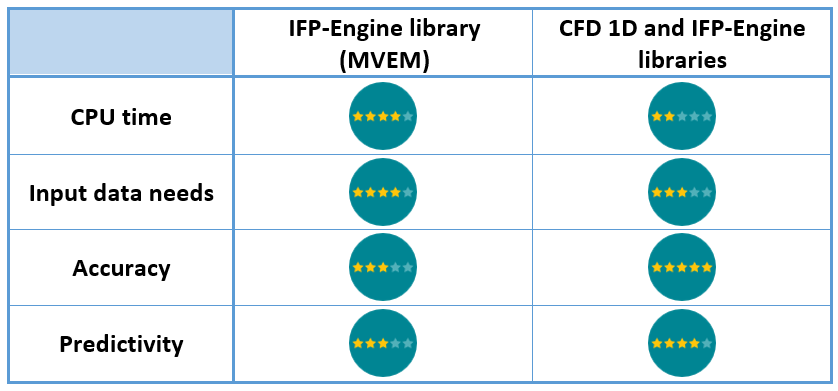 Bonus (coming in rev 16) - Assessing the vehicle underhood thermal behavior The engine is a radiative and convective heat source and will be modeled using the HEAT library components:
Bonus (coming in rev 16) - Assessing the vehicle underhood thermal behavior The engine is a radiative and convective heat source and will be modeled using the HEAT library components:
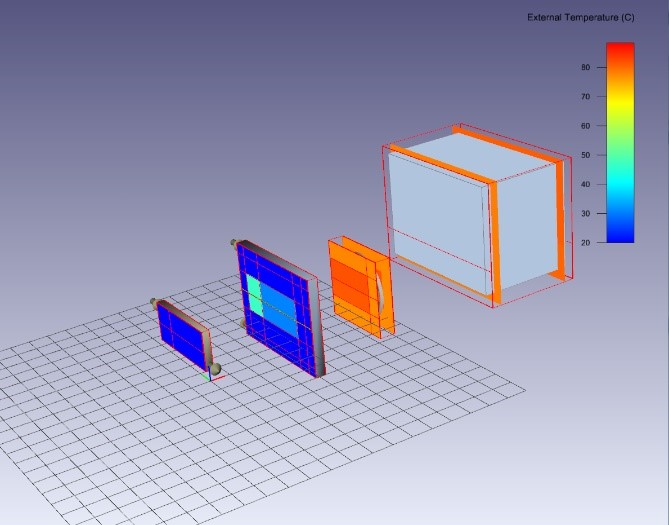
 Deutsch (Deutschland)
Deutsch (Deutschland)  English (UK)
English (UK) 


